Introduction
The C programming language is a general-purpose, operating system-agnostic, and procedural language that supports structured programming and provides low-level access to the system memory. Dennis Ritchie invented C language in 1972 at AT&T (then called Bell Laboratory), where it was implemented in the UNIX system on DEC PDP II. It was also the successor of the B programming language invented by Ken Thompson. C was designed to overcome the problems encountered by BASIC, B, and BPCL programming languages. By 1980, C programming Language became the most popular language for mainframes, microcomputers, and minicomputers.
Features of C Programming Language
Loved by programmers for doing low-level coding and embedded programming, C programming Language has found its way gradually into the semiconductor, hardware, and storage industries. The most important features provided by the C programming languages include:
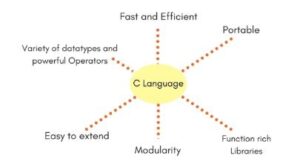
- It has inbuilt functions and operators that can solve virtually any complex problem.
- C is the combination of both low level (assembly) and high-level programming languages; also, it can be
- used to write an application and interact with low-level system memory and hardware
- It can be written on practically any operating system and even works in most handheld devices
- Programs written in C are speedy due to the support provided by its datatypes and operators
- It is easily extendable, as C++ was derived from C with additions like OOPS and other features
- The functions and operators are supported by the libraries provided by the programming language itself
Why to Learn C Programming?
C programming language is a MUST for students and working professionals to become a great Software Engineer specially when they are working in Software Development Domain. I will list down some of the key advantages of learning C Programming Language:
- Easy to learn
- Structured language
- It produces efficient programs
- It can handle low-level activities
- It can be compiled on a variety of computer platforms
Hello World using C Programming Language
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
int main ()
{
int a = 1, b=2, c=0;
int c = a + b;
printf(“Hello World”);
printf(“C = “ %d, c);
return 0;
}
Preprocessor Directives
The #include in the first line of the C programming Language is referred to as preprocessor directives. All of the preprocessors will start with the # symbol. It is the first line that is executed, having the library file ending with .h. The stdio.h in the above program will have libraries associated with print to the console output. This will also associate the program with the library. The compiler to transform the program before compilation will use the preprocessor. Macros are also similar to preprocessors, but they are all user-defined and help in expanding the values in all places in the program.
For example:
#define AREA=354;
This will substitute the variable AREA with 354 everywhere in the program and requires less effort by the programmers in the event a change is needed in the future.
Header Files
There are some standard header files provided by the language, which can be used in the program to do mathematical or logical calculations or even print to the console or files. In the above example, you have used printf function, which prints the output to the console. The stdio.h header file will have relevant or associated code for printing the output to the console, so it has to be included upfront in the program for execution.
main() function
This is an important function in the C programming language within which the content of the program or logic or calculation will be written. The main can have return types, and in the above example, it has an integer as the return types.
Compiling a C Programming Language:
There are multiple ways to compile a C programming Language. You can either use freely available editors provided by Turbo C. You can download the Turbo C editor over the internet; use it to write a program and compile using the Compile (Alt+ F9) option, and execute using Run (Ctrl + F9). The Turbo C editor is suitable for beginners, as the IDE is user-friendly. However, if you don’t have any IDEs (for example, if you’d like to execute a C program in Non-GUI environments like UNIX or Linux), you can use the following command:
$ gcc helloworld.c
$ . /a.out
Data Types
Data types are nothing but how the programmers enter, store, and manipulate data in the program. Like all other languages, C has a variety of data types, and they are mainly classified as primary datatypes, derived data types, and user-defined data types.
Primary data types are the ones that are a fundamental part of C programming language and are mostly straightforward to use (they are int, char, float, and void). Int is used to hold whole numbers and can take values like zero, positive, or negative, but it can’t contain negative values. Float and double are used to hold real numbers, and they differ from each other in byte size. Similarly, int also can handle longer and shorter ranges, which are called short and long. The table below summarizes the different data types and the size each holds in memory.
Derived data types are primitive data types forming new data structures called arrays, functions, and C pointers. For example, an array can contain a homogenous set of primitive data types like int, float, or double and can now act as a new data type in C programming language. Functions in C are both user-defined and standard library functions like scanf(), printf(), gets() and puts().
User-defined data types are defined by users and are usually a combination of data types or heterogeneous data types. For example, a structure may contain:
struct employee
{
char name[100];
int empid;
float salary;
}
With the above structure in place, the user can now define a user-defined data type as follows:
struct employee info;
Operators in C
Operators are symbols used to perform mathematical or logical operations on data. The following is the category of operators present in C:
- Arithmetic Operators
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Ternary or Conditional Operators
- Assignment Operator
The precedence of the operators will specify which will be evaluated first. For example:
int a=10+10*30
The result of the above statement is 310 because the multiplication operator is evaluated first, followed by addition.
Constants
Constants are different from variables, as the value can’t be changed during the due course of the program. There are different types of constants in the C programming language:
Decimal
Real or Floating Point
Hexadecimal
Octal
Character
String
Control Statements
Control statements are the ones that specify the program flow or the order in which the steps or instructions need to be executed. They perform the task of decision making, depending on the conditions specified in the program. There are four types of control statements in the C programming language:
Decision making
Selection
Iteration
Jump
Decision-making statements decide the flow of the program based on logical conditions like OR, AND, and NOT. The set of statements that are nested below the decision-making statements are executed based on the logical criteria met. The if and if-else (and nested if-else) are sets of decision-making statements in C.
Selection statements are based on case switch keywords. If the condition specified in the case keyword is met, then the statements below the case will be executed, and else switch statements will be executed. Iterations statements (or loops) are statements that repeat the set of instructions present inside the blocks until the condition is met. The looping statements in C programming language are while, do-while, while do, and for loop.
A counter is usually incremented or decremented inside the looping or iterative statements to make sure the loop exits when the condition is met. Jump statements are GOTO statements that can abruptly change the course of the program to execute different sets of statements mentioned in the GOTO statement. Generally, GOTO statements are not recommended in the program, as it would be difficult to predict the flow of the program in run time.
Audience
This tutorial is designed for software programmers with a need to understand the C programming language starting from scratch. This C tutorial will give you enough understanding on C programming language from where you can take yourself to higher level of expertise.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding with this tutorial, you should have a basic understanding of Computer Programming terminologies. A basic understanding of any of the programming languages will help you in understanding the C programming concepts and move fast on the learning track.